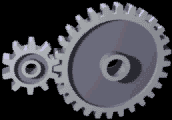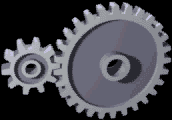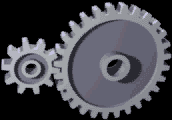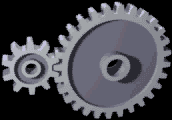
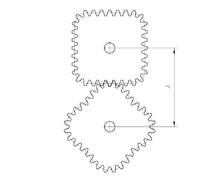
Two gears are in contact transmits the rotational movement. Smaller gears move faster, but has a lower torque. A great rotating gears lower, but have a higher torque. Large rotary speed and torque are both proportional
Gear is part of a rotating machine is useful for transmitting power. The gears have teeth that are in contact with the teeth of the other gears. Two or more gears that intersect and work together referred to as transmission gears, and can produce a mechanical advantage through a gear ratio. The gears are able to change the rotational speed, torque and direction of power over resources. Not all gears gears related to the others; one case was a couple of gears and pinion are sourced from or result in translation style, not the style of rotation.
Analog gear transmission with a belt and pulley transmission, gear transmission advantage of the belt and pulley is where the teeth are able to prevent slippage, and the transmitted power is greater. However, gears transmit power can not be done as far as wheels and pulley transmission system unless there is a lot of gear involved.
When two gears with the same number of teeth that are not combined, the mechanical advantage can be obtained, both the rotational speed and torque, which can be calculated by a simple equation. Gear with number of teeth greater role in reducing the rotational speed but increase the torque.
Careful speed ratio based on the number of teeth of the gears is a privilege that beat another transmission mechanism (eg belts and pulleys). Precision machines such as clocks tanganmengambil many benefits of rotational speed ratio of this right. In cases where resources and adjacent loads, gear has advantages because it can be designed in small size. Disadvantages of the gears is a more expensive manufacturing costs and make the necessary lubrication higher operating costs.
Ancient Greek scientist Archimedes was the first to develop dalamilmu gears mechanics in school alexandria in the third century BC. The Antikythera mechanism is an example of the application of complex gear first, which is designed to calculate astronomical positions. This mechanism is expected processing time between 150 and 100 BC
Types of gears
1 Spur
Spur gears are the simplest, consisting of a cylinder or disk with the teeth formed radially. The tip of the teeth are straight and arranged parallel to the axis of rotation. This gear can only be connected in parallel. Example: At the gear ratio Motor 2 gears in
The gears (or internal gear, internal gear) is the gear teeth located on the inside of the cylindrical gears. Unlike the external gears have teeth on the outer cylinder. Internal gears do not change the direction of rotation.
3 helical gears
Helical gears (helical gear) is a refinement of the spur. The ends of the teeth are not parallel to the axis of rotation, but arranged tilted at a certain degree. Because the angled teeth, it causes the gear to look like teeth are angled cause a meeting between the teeth become gradually so that the movement of the gears is smooth and minimal vibration. Unlike the spur where the meeting between his teeth done directly meet the space between the teeth so menyebabkn stress and vibration. Helical gears are able to operate at higher speeds than a spur for the high speed turn can cause the spur to experience high vibration. Spur better used on a low round. Said to be high if the rotational speed of the pitch exceeds the linear velocity of 25 m / sec
Helical gears can be put together in parallel and transverse. Commonly performed in parallel arrangement, and the arrangement of the cross-section is usually referred to as the skew. Example: Secondary Primary Teeth
4 double helical gears
Double helical gears (double helical gear) or herringbone gears arises because of the problem of axial thrust (axial thrust) of a single helical gears. Double helical gear has two pairs of V-shaped teeth so as if there are two helical gears are put together. This will cause the axial thrust mutually exclusive. Double helical gears are more difficult to be made because of the complexity of its shape.
5. bevel gears
Bevel gears (bevel gear) shaped like a truncated cone with teeth formed on its surface. When two bevel gears mersinggungan, the imaginary cone end point will be at one point, and the shaft axis will intersect. The angle between the two bevel gears can be any number except 0 and 180. Bevel gears can be straight shaped like a spur or helical gears spiral. The advantages and disadvantages just like the comparison between the spur and helical gears.
6 hypoid gears
Hypoid gears like bevel gears, but the two do not intersect its axis.
7 gears crown
Crown gears (crown gear) is one form of a bevel gear teeth are not parallel and angled to the axis. Teeth shape resembles a crown. Crown gear can only be accurately paired with bevel or spur gears.
8. worm gears
(worm gear) resembles a screw-shaped rod paired with a regular or spur gears. Worm gear is one of the easiest ways to get a high ratio of torque and low rotational speed. Typically, couples spur or helical gears have a maximum ratio of 10: 1, while the ratio of worm gear capable of achieving 500: 1 Losses of worm gear is the friction that makes the worm gear has low efficiency and thus require lubrication
Worm gear similar to helical gears, except the teeth angle approaching 90 degrees, and typically an elongated body shape follows the axial direction. If there is at least one tooth that surrounds the body reaches the round gear, then it is a worm gear. If not, then it is a helical gears. Worm gear having at least one tooth that is able to surround his body several times. The number of teeth on the worm gear is usually referred to as a thread.
In a worm gear pair, the stem can always move the spur gear. Rare is the spur that is capable of moving the worm gear. That is to say that the worm gear pair is one-way transmission. Example: speedo meter
9. non-circular gears
Non-circular gears are designed for specific purposes. Regular gear is designed to optimize power transmission with minimal vibration and wear, non-circular gears are designed for the variation ratio, oscillation, and so on.
10 pinion gears
The pair consists of a pinion gear gear, which is called the pinion, and a serrated stem called the rack. The combination of rack and pinion produces a different torque transmission mechanism; torque transmitted from style to style swivel translation or vice versa. When the pinion rotates, the rack will move straight. This mechanism is used in some types of vehicles to change the rotation of the steering wheel vehicle into a movement to the right and to the left of the rack so that the wheels change direction.
11. gears episiklik
Episiklik gears (or epicyclic gear planetary gear) is a combination of gears that resemble the movement of the planets and the sun gear of this type are used to change the ratio of the axial rotation axis, not parallel. The combination of multiple gears episiklik by stopping movement mechanism generates an internal gear ratio can change. This mechanism is used in vehicles with automatic transmission
Gear is part of a rotating machine is useful for transmitting power. The gears have teeth that are in contact with the teeth of the other gears. Two or more gears that intersect and work together referred to as transmission gears, and can produce a mechanical advantage through a gear ratio. The gears are able to change the rotational speed, torque and direction of power over resources. Not all gears gears related to the others; one case was a couple of gears and pinion are sourced from or result in translation style, not the style of rotation.
Analog gear transmission with a belt and pulley transmission, gear transmission advantage of the belt and pulley is where the teeth are able to prevent slippage, and the transmitted power is greater. However, gears transmit power can not be done as far as wheels and pulley transmission system unless there is a lot of gear involved.
When two gears with the same number of teeth that are not combined, the mechanical advantage can be obtained, both the rotational speed and torque, which can be calculated by a simple equation. Gear with number of teeth greater role in reducing the rotational speed but increase the torque.
Careful speed ratio based on the number of teeth of the gears is a privilege that beat another transmission mechanism (eg belts and pulleys). Precision machines such as clocks tanganmengambil many benefits of rotational speed ratio of this right. In cases where resources and adjacent loads, gear has advantages because it can be designed in small size. Disadvantages of the gears is a more expensive manufacturing costs and make the necessary lubrication higher operating costs.
Ancient Greek scientist Archimedes was the first to develop dalamilmu gears mechanics in school alexandria in the third century BC. The Antikythera mechanism is an example of the application of complex gear first, which is designed to calculate astronomical positions. This mechanism is expected processing time between 150 and 100 BC
Types of gears
1 Spur
Spur gears are the simplest, consisting of a cylinder or disk with the teeth formed radially. The tip of the teeth are straight and arranged parallel to the axis of rotation. This gear can only be connected in parallel. Example: At the gear ratio Motor 2 gears in
The gears (or internal gear, internal gear) is the gear teeth located on the inside of the cylindrical gears. Unlike the external gears have teeth on the outer cylinder. Internal gears do not change the direction of rotation.
 |
| Gears in |
Helical gears (helical gear) is a refinement of the spur. The ends of the teeth are not parallel to the axis of rotation, but arranged tilted at a certain degree. Because the angled teeth, it causes the gear to look like teeth are angled cause a meeting between the teeth become gradually so that the movement of the gears is smooth and minimal vibration. Unlike the spur where the meeting between his teeth done directly meet the space between the teeth so menyebabkn stress and vibration. Helical gears are able to operate at higher speeds than a spur for the high speed turn can cause the spur to experience high vibration. Spur better used on a low round. Said to be high if the rotational speed of the pitch exceeds the linear velocity of 25 m / sec
 |
| Helical gears Above: paralelBawah allusions: allusions cross |
4 double helical gears
Double helical gears (double helical gear) or herringbone gears arises because of the problem of axial thrust (axial thrust) of a single helical gears. Double helical gear has two pairs of V-shaped teeth so as if there are two helical gears are put together. This will cause the axial thrust mutually exclusive. Double helical gears are more difficult to be made because of the complexity of its shape.
 |
| Double helical gears |
Bevel gears (bevel gear) shaped like a truncated cone with teeth formed on its surface. When two bevel gears mersinggungan, the imaginary cone end point will be at one point, and the shaft axis will intersect. The angle between the two bevel gears can be any number except 0 and 180. Bevel gears can be straight shaped like a spur or helical gears spiral. The advantages and disadvantages just like the comparison between the spur and helical gears.
6 hypoid gears
Hypoid gears like bevel gears, but the two do not intersect its axis.
Crown gears (crown gear) is one form of a bevel gear teeth are not parallel and angled to the axis. Teeth shape resembles a crown. Crown gear can only be accurately paired with bevel or spur gears.
(worm gear) resembles a screw-shaped rod paired with a regular or spur gears. Worm gear is one of the easiest ways to get a high ratio of torque and low rotational speed. Typically, couples spur or helical gears have a maximum ratio of 10: 1, while the ratio of worm gear capable of achieving 500: 1 Losses of worm gear is the friction that makes the worm gear has low efficiency and thus require lubrication
Worm gear similar to helical gears, except the teeth angle approaching 90 degrees, and typically an elongated body shape follows the axial direction. If there is at least one tooth that surrounds the body reaches the round gear, then it is a worm gear. If not, then it is a helical gears. Worm gear having at least one tooth that is able to surround his body several times. The number of teeth on the worm gear is usually referred to as a thread.
In a worm gear pair, the stem can always move the spur gear. Rare is the spur that is capable of moving the worm gear. That is to say that the worm gear pair is one-way transmission. Example: speedo meter
 |
| Worm gear with 4 threads |
Non-circular gears are designed for specific purposes. Regular gear is designed to optimize power transmission with minimal vibration and wear, non-circular gears are designed for the variation ratio, oscillation, and so on.
The pair consists of a pinion gear gear, which is called the pinion, and a serrated stem called the rack. The combination of rack and pinion produces a different torque transmission mechanism; torque transmitted from style to style swivel translation or vice versa. When the pinion rotates, the rack will move straight. This mechanism is used in some types of vehicles to change the rotation of the steering wheel vehicle into a movement to the right and to the left of the rack so that the wheels change direction.
Episiklik gears (or epicyclic gear planetary gear) is a combination of gears that resemble the movement of the planets and the sun gear of this type are used to change the ratio of the axial rotation axis, not parallel. The combination of multiple gears episiklik by stopping movement mechanism generates an internal gear ratio can change. This mechanism is used in vehicles with automatic transmission
 |
| Illustration of round gears episiklik. Note the difference in rotational speed are marked with red on the shaft of the sun gear and the planet |
Simple planetary gears can be found at the time of the revolution in England when the planetary gear mechanism that form the center of the sun gear and the gear that revolves around a planet, a major part of this Part steam engine change the style of translation into rotation, which then can be used for various needs.